How AI is impacting the Banking Sector - US versus French Banks
In a recent report by Citigroup, a global investment firm, it was concluded that the banking industry will be heavily impacted by the use of AI. The report indicates that 54% of jobs in banking are at risk of being displaced by AI, and an additional 12% could be enhanced by AI.
In Citigroup's new report, the banking industry tops the list with 54% of jobs at risk, followed by insurance (48%) and energy (43%). The report suggests that banks will need to hire new roles like AI managers and compliance officers, and estimates that AI could add $170B or 9% to the global banking sector's profit pool by 2028. While automation may impact traditional tasks, new AI-first roles are expected to lead to a shift in job responsibilities rather than significant headcount cuts.
Citigroup’s AI Strategy or How is Citigroup Deploying AI
According to Bloomberg, Citi planned to implement generative AI technology for its 40,000 developers. The world’s biggest bank had already used automation to analyse a vast set of new capital regulations, enabling it to carefully examine 1,089 pages of these complex rules. Citi's risk management and compliance team were then able to evaluate the potential impacts of the proposed regulatory changes.
During the bank's digital money symposium last Thursday, CEO Jane Fraser outlined the banking giant's strategic priorities regarding AI adoption. Fraser emphasised that its main focus is on transitioning AI technologies from the research and development phase to practical implementation across various operational domains, stating, “Our focus now is on taking it from the lab to the factory floor.” She highlighted two key areas where Citi aims to leverage AI capabilities. The bank is exploring the potential of AI to provide personalized investment recommendations tailored to the unique needs and preferences of its wealth management clients. Additionally, the CEO underscored Citi's commitment to bolstering its cybersecurity offerings through the integration of AI solutions.
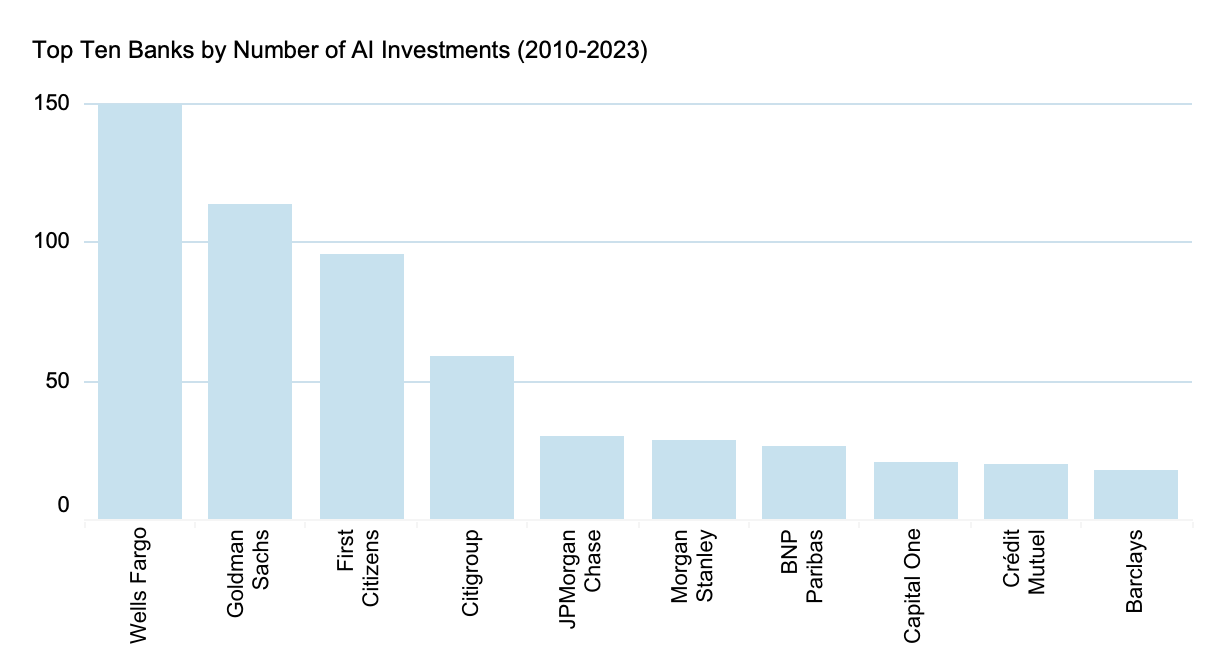
As outlined in the blog “Connecting the dots in Fintech”, the analysis shows that North American banks, especially those from the U.S., are performing better than their European counterparts in respect to AI research. They have produced 80% of all AI research and filed 99% of all AI patents recently.
Notably, JPMorgan Chase, Capital One, Wells Fargo, and Canadian banks like RBC and TD Bank consistently lead in the AI sector. Their strong presence in AI and talent acquisition suggests they are establishing a significant advantage over others. On the other hand, AI innovation in European banks is significantly behind. Although BNP Paribas is the leading French bank in AI, it does not make the global top 10. The UK is also less prominent in AI, except for Barclays in AI ventures. Nevertheless, there is an opportunity for a European AI champion, potentially a Spanish bank like BBVA.
French Banks vs. US Banks: Differences in AI Adoption
French banks have been more cautious in adopting AI compared to US banks. This is due to stricter data privacy laws, such as GDPR, and a cultural preference for personal relationships in customer interaction.
But AI is becoming more prevalent among French banks; with Banks typically spending between 3 and 5 billion euros per year on IT expenses alone. BNP Paribas, for example, employs 47,000 employees in its IT services, almost a quarter of its total workforce. According to BNP Paribas, mastering and implementing artificial intelligence offers multiple benefits to the French bank such as understanding customers, developing tailored products and services, increasing operational efficiency, and detecting cybersecurity risks. BNP Paribas has deployed use cases leveraging AI across the various BNP Paribas businesses across 3 main functions:
1. Sales and customer experience
2. Operational efficiency
3. Risk management
AI is leveraged to improve Sales and customer experience at BNP Paribas, for example for their Wealth Management business: analysis of client transaction history and prediction of interest for a purchase or sale recommendation. For Retail: generation of marketing campaigns by almost 15% by AI; and provision of a virtual assistant in Belgium with personalised responses 24/7 and roll-out of its AI Assistant NOA.
By rapidly collecting and processing large volumes of data, AI can also improve operational efficiency by automating repetitive tasks, freeing up staff time for higher value-added tasks such as advice, monitoring or analysis. An example of their Leasing business: is indexing and archiving a large volume of documents using machine learning, which reduces the processing time for a grant request from 2 hours to 30 minutes and allows the customer to benefit from a response faster.
From a Risk Management perspective, AI is a powerful tool for detecting and preventing major risks for the Bank and its clients. For example, it helps experts analyse data more quickly and efficiently to detect anomalous behaviour, prevent fraud and alert customers.
French banks are increasingly realising the potential benefits of AI. It can improve operational efficiency, detect fraud more effectively, and enhance the customer experience. As a result, we can expect to see a gradual increase in AI adoption by French banks in the coming years as they navigate the regulatory challenges and cultural considerations to leverage the full potential of artificial intelligence.
US banks have already made substantial investments in AI technologies over the last few years, positioning themselves as frontrunners in the race compared to their European counterparts. While European banks are also adopting AI, the scale and pace of implementation in the US have propelled them ahead in the AI race within the banking sector.